Otoplasty Ear
Conveniently Located to Serve the Dallas, Fort Worth, Collin, and Denton Counties.



What is An Otoplasty?
Otoplasty means reshaping the ears, and this can be performed with surgery (most of the time) or non-surgically (in infants less than 6-8 weeks old). Otoplasty does not generally refer to microtia repair, which is a deformity of infants where the ear may be severely deformed or missing large components. Microtia often also involves abnormal development of the ear canal and other structures, not just the external ear.

Many people are born with ears that they feel are too large, or protrude too far from the side of the head. The medical term for this problem is prominauris or prominotia. This can have a significant impact on a person’s self image, and may even be a source of teasing in young children and adolescents. Luckily, we have many great options to treat ear deformities. Otoplasty means reshaping the ears, and is commonly referred to as “pinning back” or “reducing” the ears.
Each patient presents a unique case as no one’s ears are the same, often differing slightly even in the same patient. For this reason, meticulous attention to detail must be undertaken to achieve symmetry between the two ears. Dr. Cain and Dr. Richardson both have specialized training in performing surgery on the ears and can assess your concerns and recommend which technique would provide the desired results during your consultation.
Otoplasty is generally performed under IV sedation in our private surgical center, and usually takes 1.5 – 2 hours to complete. Patients are discharged after surgery and follow up in clinic on the first day after the procedure for dressing removal and a post-operative checkup. The doctors and nurses provide detailed instructions on how to care for the ears after the procedure, but there is very little maintenance involved other than protecting the ears for the first few weeks after surgery. This procedure is life-changing and has an extremely high satisfaction rate!
How is an otoplasty performed?
Otoplasty is generally performed by making incisions in the crease behind the ear, to hide any incision lines. The cartilage in the ears is typically weakened and reshaped, and excess skin and cartilage may be removed in order to allow the ears to be repositioned to the desired location. In some cases, no cartilage needs to be removed, and the ear may be reshaped and positioned with sutures alone. In young infants less than 6-8 weeks old, the Ear Well device can be used to reshape the ears non-surgically. After that time frame, the ear is no longer pliable enough to result in significant long-term non-surgical reshaping improvements.
In infants treated with the Ear Well reshaping device, there is no pain involved. In children and adults treated surgically with otoplasty, there is some mild discomfort postoperatively, but there is usually not much pain. Most patients take a small amount of pain medicine only for a day or two. Surgery is always performed under general anesthesia in small children. In teenagers and adults, we almost always perform otoplasty under IV sedation so that patients are comfortable the entire time. Pure local anesthesia is an option, but not generally preferred for either the patient or the surgeon.
How is otoplasty different from microtia repair?
As described above, microtia repair involves a team of pediatric otolaryngologists, audiologists, and possibly otologists or plastic surgeons due to all the different deformities that may be involved. Otoplasty involves simply reshaping the external ear through the means described above.
At what age should a patient have an otoplasty?
Otoplasty is commonly performed at several different points in time. While not technically an otoplasty procedure, ear reshaping can be performed in infants using the Ear Well device if started very early (less than 6-8 weeks of age). With this treatment, the sooner the process starts the better. We recommend placing the device within the first few days of life if at all possible. More details about this procedure are described below.
For surgical otoplasty, the primary time frames for this are around the age of 5-6 years old, before children start school. This is because the ear is almost fully adult size by this age, and prevents the child becoming aware of their deformity by getting teased at school. Another most common time frame is in the early teenage years around the age of 13-15 as adolescents become aware of the cosmetic deformity in puberty. They begin to notice their own prominent ears and ask their parents about correction. Finally, many adults seek out otoplasty because they may have the financial means and ability to have a surgical procedure that they have been wanting most of their lives. There is no age limit for an otoplasty.
Does insurance pay for an otoplasty?
In some cases, yes. Most major insurance plans will help cover the costs of otoplasty surgery in young children around the age of 5-6. By the teenage years, many insurance plans will deem this to be a cosmetic issue that they will not cover. In adults, the procedure is always deemed cosmetic in nature, so insurance is not involved. Most insurance programs will help with paying for the Ear Well device, but not always. We are happy to help look into your insurance benefits to assist you if needed.
What is the Ear Well procedure?
The Ear Well is a device designed to reshape the ears of young infants. This device is ideally placed within the first few days of life, but can be expected to achieve results in many cases up to around 6-8 weeks of life. The sooner this device is placed on an ear with a deformity, the better the results are likely to be. We are an approved Ear Well provider. The device holds the ear in a fixed position so that as the cartilage matures over the first few weeks, the ear will hopefully hold its shape permanently. The device usually stays in place for about six weeks with periodic checkups while the device is in place. Success rates are around 90% with the Ear Well, but decline as the baby gets older. If your child has an ear deformity and would like to discuss the Ear Well device, please contact us as soon as possible. We do have the device in stock and can hopefully fit your baby within a few days in order to achieve the best possible results without surgery. To learn more about Ear Well, watch the video below or CLICK HERE to visit the manufacturer’s website.

“Amazing Otoplasty Experience”
“Amazing Otoplasty Experience. I am glad I chose Dr Richardson. He did an amazing otoplasty procedure and I would highly recommend him. Staff was perfect. Dr. Richardson was very transparent, honest, and made me feel very comfortable.”
(REALSELF)
What are the contraindications to otoplasty?
Contraindications to otoplasty are similar to other surgical procedures. Any condition that might make anesthesia unsafe would be a concern. This includes severe heart, lung, kidney, and other diseases, but most mild conditions are not a problem. Patients with bleeding disorders or wound healing problems like collagen vascular diseases might not be a candidate either. We will review your medical history, and in some cases, may require a pre-operative workup and evaluation with your primary care doctor.
What can I expect after otoplasty?
Patients should expect some mild discomfort for a few days after surgery. Some redness and swelling of the ears is totally normal. This takes several weeks to resolve completely, but is mostly gone after the first 7-10 days in most cases. There may be some numbness of the ears that takes time to resolve completely. Some mild relaxation of the otoplasty correction is possible over time, so in some cases, we may very slightly “over-correct” the ears to account for this relaxation over the first few months.
What are the risks of otoplasty? Is otoplasty safe?
The risks of otoplasty surgery include bleeding, scarring, infection, numbness, cosmetic dissatisfaction, and the possible need for future surgery. Complications are rare and satisfaction rates are high. We have many techniques and instructions for avoiding complications or problems post-operatively, and walk patients through every step of the process in a detailed fashion.
What is the downtime with otoplasty?
Otoplasty requires care to the ears postoperatively. Most patients are back at work and/or school within a week after surgery, but are required to refrain from any strenuous activity for at least two weeks after surgery. Patients also have to be very careful about getting hit in the ears for at least six weeks postoperatively, and possibly longer.
Who is qualified to perform otoplasty?
Otoplasty surgery should be performed by a board-certified surgeon trained in the United States or Canada. Most surgeons performing otoplasty procedures are fellowship-trained in either facial plastic surgery, general plastic surgery, or pediatric otolaryngology. As fellowship-trained facial plastic surgeons, both Dr. Richardson and Dr. Cain are experts in otoplasty and perform this procedure commonly in our practice.
What are the success rates of otoplasty?
Otoplasty is generally very successful and revision surgery rates are very low. Patient satisfaction rates are also generally very high, which makes this one of our favorite procedures. We love helping patients feel better about themselves. Ear surgery has a 92% “Worth It” rating on RealSelf.com.
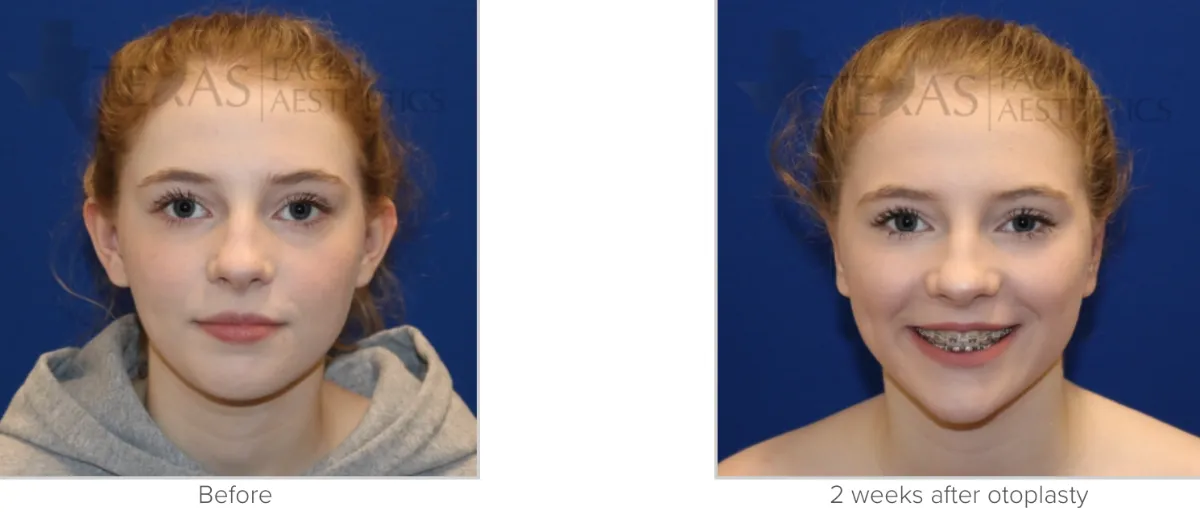
*Individual Results may vary.
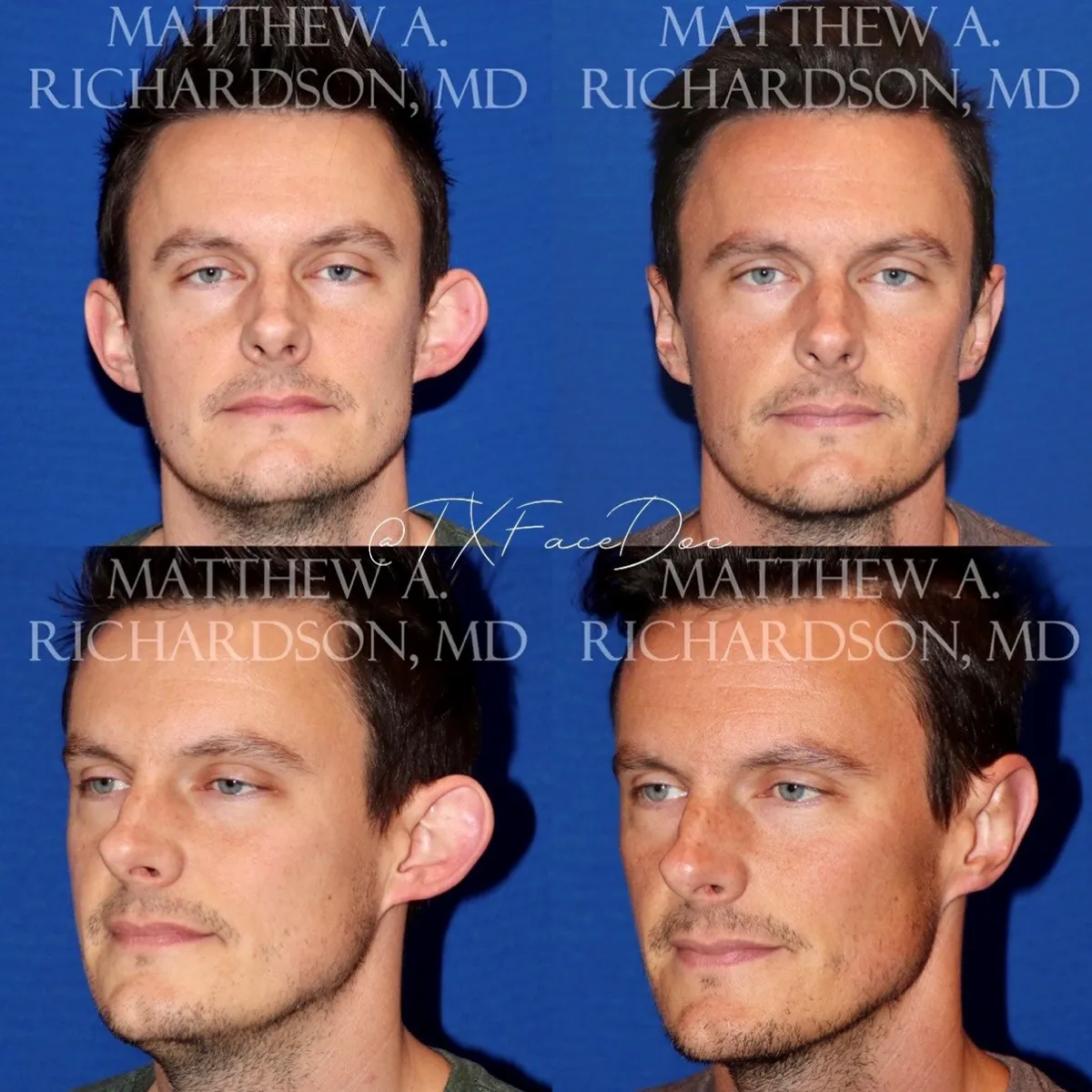
Real Patient Photo Gallery
View before-and-after pictures of real patients
How can I set up An EAr Pinning Surgery Consultation?
Call or text Texas Facial Aesthetics at 469-362-6975 to set up a consultation with either Dr. Matthew Richardson or Dr. Jordan Cain. You can also email us at info@txfaces.com for more information.
